Description
Laser Cutting Steel Panels Laser Division Stainless Steel Plates Metal Media
Laser Cutting Steel Panels Is For The Material Of The Steel Panels To Be Cut, Generally Refers To The Process Of Melting, Blowing Slag And Separating Steel Panels By Mixing Combustion Of Industrial Gas And Oxygen And Reaching The Cutting Temperature.
Laser Division Stainless Steel Plates Refers To The Process Of Using Natural Gas Flame (Oxygen-Natural Gas) To Preheat The Cut Stainless Steel Plates To The Burning Point That Can Be Burned Violently, And Then Release High-Pressure Oxygen Flow To Make The Stainless Steel Plates Further Oxidize Violently And Blow Off The Burning Slag To Form a Notch.
Laser Cut Metal Media Flame Temperature Of Normal Natural Gas Combustion With Oxygen Can Not Reach The Flame Temperature Of Acetylene Combustion With Oxygen. It Is Necessary To Add Temperature-Increasing And Combustion-Supporting Additives To Achieve The Cutting Temperature Required For Natural Gas Cutting.
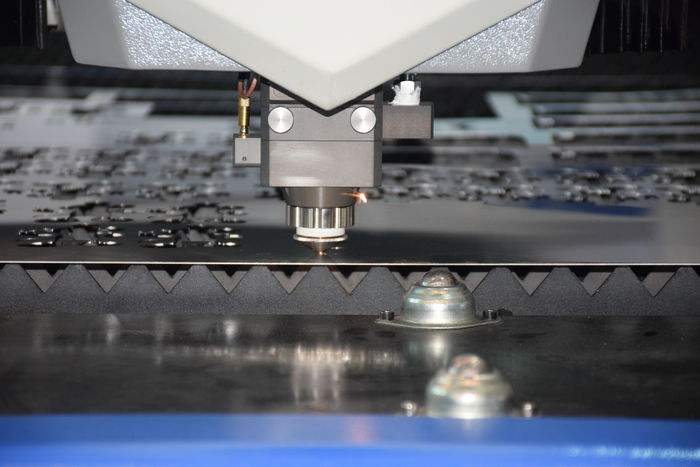
Laser Cutting Steel Panels Working Principle
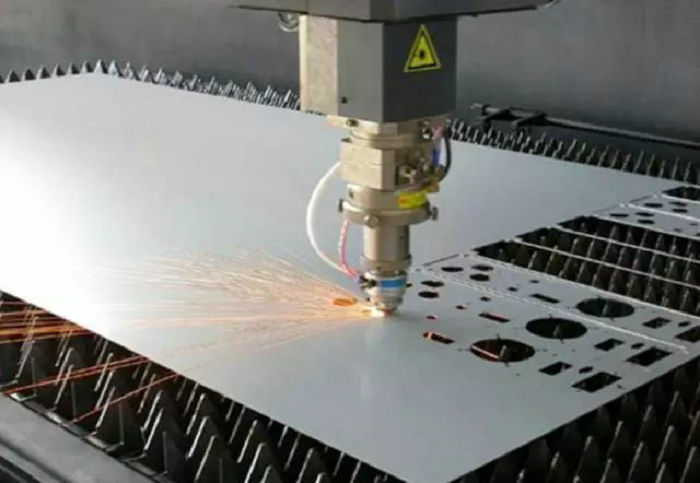
The Cutting Material Is Irradiated By High Power Density Laser Beam, So That The Material Is Quickly Heated To Vaporization Temperature, And Evaporation Forms a Hole. With The Beam Moving To The Material, The Hole Continuously Forms a Narrow Width (Such As About 0.1mm) Slit To Complete The Cutting Of The Material.
Laser Cutting Is To Use a Focused High Power Density Laser Beam To Irradiate The Workpiece, So That The Irradiated Material Can Melt, Vaporize, Ablate Or Reach The Ignition Point Rapidly. At The Same Time, The Melted Material Can Be Blown Away By High-Speed Airflow In The Coaxial Direction Of The Laser Beam, So That The Workpiece Can Be Cut Off. Laser Cutting Is One Of The Hot Cutting Methods.
Laser Cutting Steel Plate Brief Introduction
The Price Of Laser Cutting Equipment Is Quite Expensive, About 1.5 Million Yuan Or More. With The Continuous Development Of The Tank Industry, More And More Industries And Enterprises Have Applied The Tank Industry, And More And More Enterprises Have Entered The Tank Industry. However, It Is Feasible To Use This Equipment In Large-Scale Production Because Of The Reduction Of The Cost Of Subsequent Process Treatment.
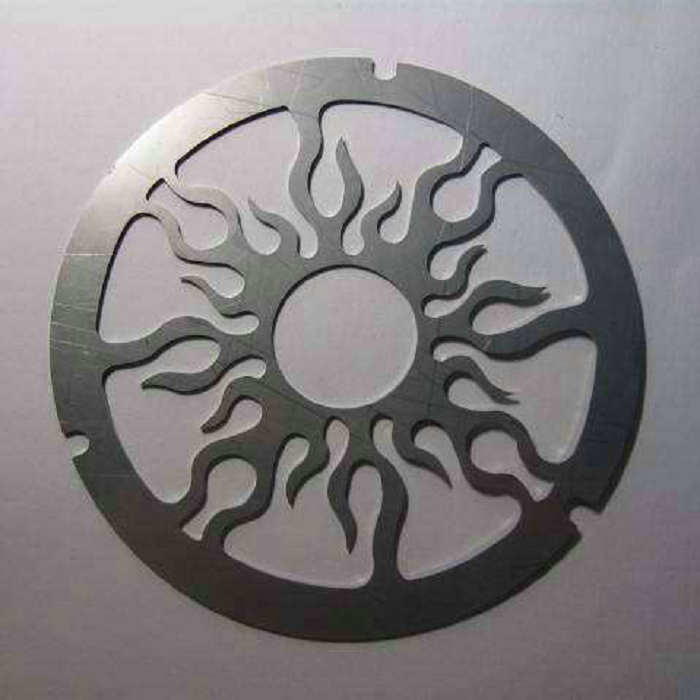
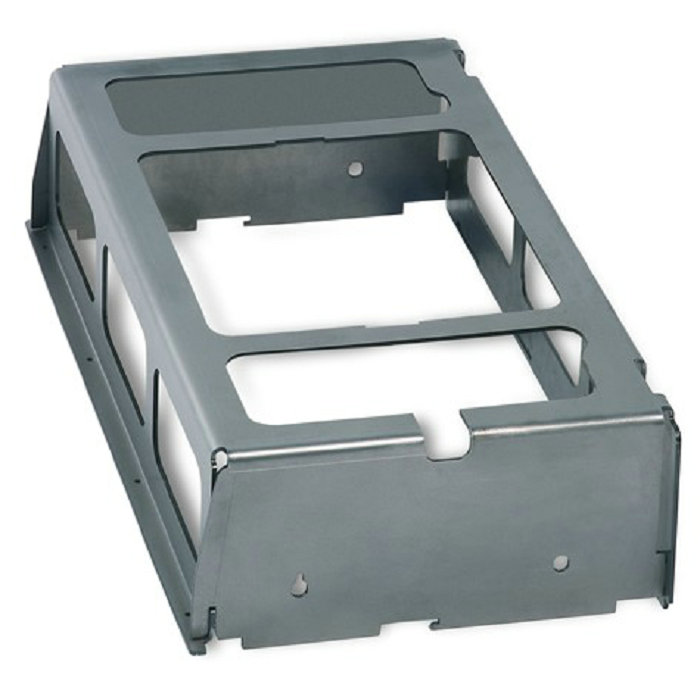
Because There Is No Tool Processing Cost, Laser Cutting Equipment Is Also Suitable For The Production Of Small Batches Of Components Of Various Sizes That Could Not Be Processed Before. Laser Cutting Equipment Usually Adopts Computerized Digital Control Technology (CNC) Device. With This Device, The Cutting Data Can Be Received From The Computer Aided Design (CAD) Workstation By Telephone Line.
Laser Cutting Can Be Divided Into Four Categories: Laser Vaporization Cutting, Laser Melting Cutting, Laser Oxygen Cutting, Laser Scratching And Controlled Fracture.
Laser Vaporization Cutting
Using High Energy Density Laser Beam To Heat The Workpiece, The Temperature Rises Rapidly And Reaches The Boiling Point Of The Material In a Very Short Time. The Material Begins To Vaporize And Forms Vapor. These Vapors Eject At a Very High Speed, While The Vapor Ejects At The Same Time, a Notch Is Formed On The Material. The Heat Of Vaporization Of Materials Is Generally Very Large, So Laser Vaporization Cutting Requires a Lot Of Power And Power Density.
Laser Vaporization Cutting Is Mostly Used For Cutting Very Thin Metal Materials And Non-Metallic Materials (Such As Paper, Cloth, Wood, Plastics And Rubber, Etc.).
Laser Melting Cutting
During Laser Melting And Cutting, Metal Materials Are Melted By Laser Heating, And Then Non-Oxidizing Gases (Ar, He, n, Etc.) Are Injected Through Nozzles Coaxial With The Light Beam. The Liquid Metal Is Discharged By The Strong Pressure Of The Gases To Form An Incision. Laser Melting Cutting Does Not Need To Vaporize The Metal Completely, And The Required Energy Is Only 1/10 Of Vaporizing Cutting.
Laser Melting Cutting Is Mainly Used For Cutting Some Non-Oxidizable Materials Or Active Metals, Such As Stainless Steel, Titanium, Aluminum And Its Alloys.
Laser Oxygen Cutting
The Principle Of Laser Oxygen Cutting Is Similar To That Of Oxyacetylene Cutting. It Uses Laser As Preheating Source And Oxygen As Cutting Gas. On The One Hand, The Gas Injected Reacts With The Cutting Metal To Produce Oxidation Reaction, Which Releases a Large Amount Of Heat Of Oxidation; On The Other Hand, The Molten Oxides And Melts Are Blown Out From The Reaction Zone To Form a Notch In The Metal. Because The Oxidation Reaction In The Cutting Process Produces a Lot Of Heat, The Energy Required For Laser Oxygen Cutting Is Only 1/2 Of That For Melting Cutting, And The Cutting Speed Is Much Faster Than That Of Laser Vaporization Cutting And Melting Cutting. Laser Oxygen Cutting Is Mainly Used For Oxidizable Metal Materials Such As Carbon Steel, Titanium Steel And Heat Treatment Steel.
Laser Scratching And Controlled Fracture
Laser Scratching Is To Use High Energy Density Laser Scanning On The Surface Of Brittle Materials, So That Materials Are Heated And Evaporated Into a Small Groove, And Then Applied a Certain Pressure, Brittle Materials Will Crack Along The Groove. Laser Scratch Lasers Are Generally q-Switched Lasers And Co2 Lasers.
Controlling Fracture Is To Use The Steep Temperature Distribution Produced By Laser Grooving To Produce Local Thermal Stress In Brittle Materials, Which Can Make The Material Break Along The Groove.